Which of the Following Are Systems Bacteria Can Use to Protect Agains Invading Dna
Both bacteria and viruses are invisible to the naked centre and cause your sniff, fever or cough, and so how can nosotros tell the difference?
With bacteria rapidly developing resistance to antibiotics, it is increasingly important that we know the stardom, because viruses can't be treated with antibiotics, nor bacteria with antivirals.
Rapid and effective testing is imperative, so we can successfully treat the offending microorganism.
COVID-19 is education us the difficult fashion–nosotros have no handling for a new virus until we have anti-viral drugs and vaccines specifically targeted confronting it.
Therapies adult against an existing virus ofttimes do non work, or piece of work poorly, against a new virus. Until this fourth dimension, our best weapons are handwashing and physical distancing.
On a biological level, the main departure is that bacteria are free-living cells that can live inside or outside a body, while viruses are a non-living drove of molecules that need a host to survive.
Many leaner help us: living in our gut digesting and helping absorption of our food, fixing nitrogen and decomposing organic materials in soil. Similarly, non all viruses are bad—we at present know at that place are also beneficial viruses present in our gut, pare and blood that can impale undesirable bacteria and more unsafe viruses.
Bacteria and viruses are all around us
Bacteria and viruses may not be visible with the human eye, simply they are all around u.s. in truly staggering numbers.
In our oceans, there are 10 billion times more bacteria than at that place are stars in the universe.
The millions of viruses in the earth laid cease to end would stretch for 100 one thousand thousand low-cal years.
Microorganisms, living harmlessly on, and in our bodies, outnumber human cells by 10 to i, playing a vital role in human wellness.
Simply not all microorganisms be in harmony with usa. Pathogens are a subset of microorganisms that can cause disease and these include representatives of leaner, fungi, viruses, helminths and protozoa.
1% of the world'south known microbial population is known to be pathogenic to humans— approximately 1400 species.
What are leaner?
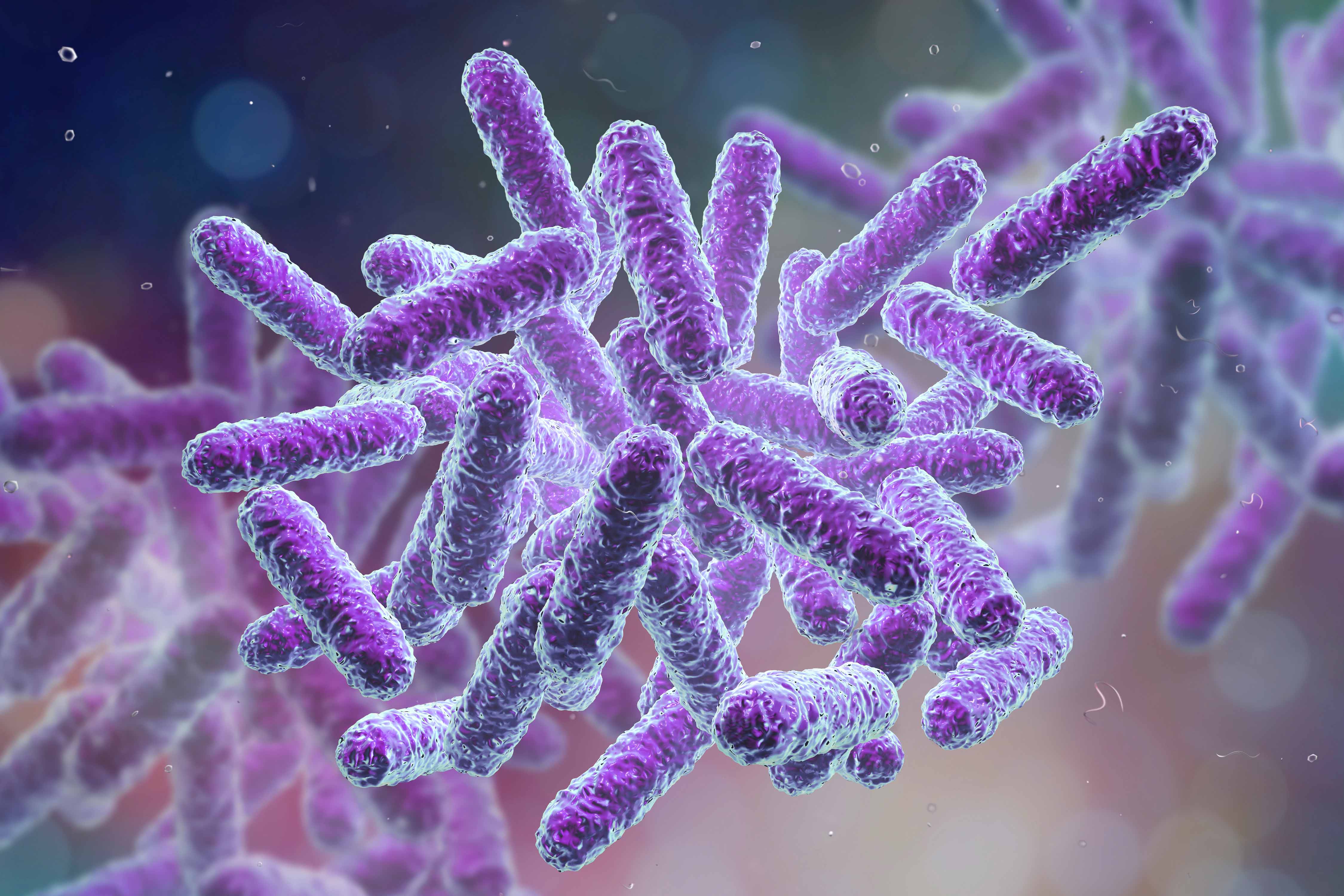
Bacteria are prokaryotes—the smallest, simplest and most aboriginal cells, with free-floating genetic material. These microscopic single-celled organisms can be rod, spiral or spherical in shape.
There are two types of bacteria: Gram-negative and Gram-positive. The key divergence is the presence of an extra outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria. Information technology's essentially an extra line of defense that makes it harder for antibiotics to penetrate, thus making Gram-negative leaner more difficult to kill and more than prone to developing resistance.
Bacteria are abundant in soil, inhabiting plant root systems to provide services like nitrogen fixing or interim every bit antifungal agents. Thermophilic (oestrus-loving) bacteria set up sulphur to produce sulphide and energy for photosynthesis in aquatic sediments or organically rich waters.

Dangerous leaner too alive in soil, a good reason to habiliment gardening gloves. The floods in northern Queensland in 2019 brought Burkholderia pseudomallei to the surface, leaner which cause a serious infection known as melioidosis.
In our bodies, bacteria inhabit the human digestion system, live on our skin and contribute to free energy metabolism, digestion, brain function and full general wellbeing. But if the balance of these leaner is tipped by a dose of antibiotics or ill-health, so gut discomfort or skin infections are common.
Infectious diseases acquired past bacteria have killed well over half of all humans who have e'er lived on Earth. Historically, bacterial infections take started major pandemics such as the bubonic plague, which is estimated to have killed l-lx per cent of the population of Europe during the Blackness Expiry in the xivth Century.
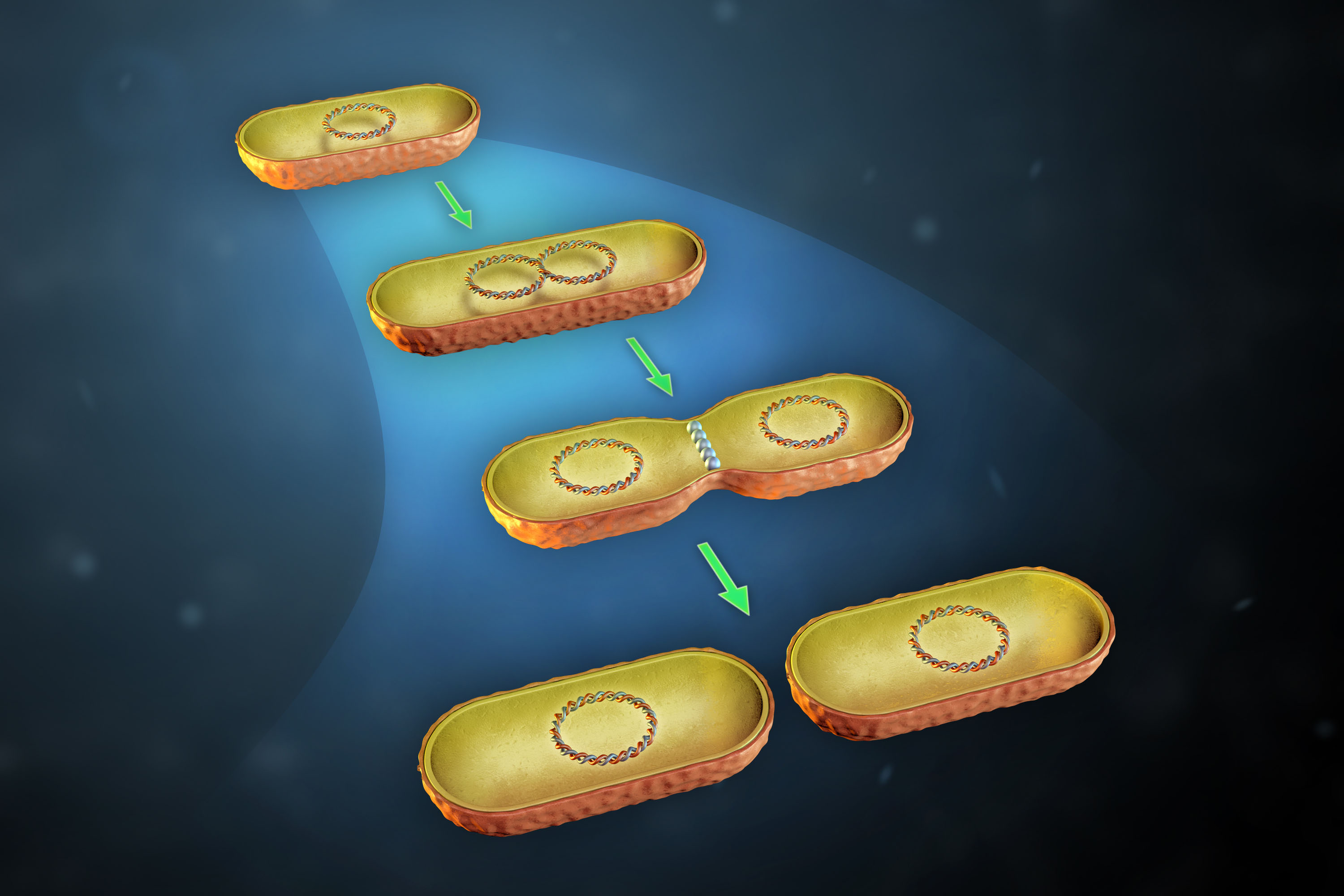
Bacteria reproduce mainly past binary fission–replicating their DNA then they take two copies on opposite sides of the cell, so growing a new cell wall down the eye to produce two daughter cells. This doubling time takes between xx minutes and an hour.
This curt generation fourth dimension allows mutations to emerge and accrue rapidly and quickly crusade significant changes in bacteria, such as resistance to antibiotics.
Communication is fundamental
Bacteria can communicate with one another by releasing chemic signalling molecules, allowing the population to human activity equally ane multicellular organism.
Depending on the density of molecules and the betoken it generates, the bacterial community tin adjust and respond to compete for resources in a process known as quorum sensing.

This ability to communicate with one another allows bacteria to coordinate gene expression, and therefore the behaviour, of the entire community.
This process gives bacteria some of the qualities of higher organisms and is a powerful weapon against antibiotics. Information technology can trigger some bacteria to close downwardly and become fallow when exposed to an antibiotic, and they are able to regenerate when the antibody is gone.
What are viruses?
Viruses are an assembly of different types of molecules that consist of genetic textile (either a single- or double-stranded DNA or RNA) with a protein glaze and sometimes a layer of fatty also (an envelope).
They can assume different shapes and sizes—spacecraft designs, spirals, cylinders and ball shapes.
Viruses that are enveloped with a layer of fatty (such equally SARS-CoV-2 which causes COVID-xix) tin can be more readily killed by uncomplicated handwashing, considering soap disrupts this fatty layer.
Viruses can't reproduce on their ain (different leaner) so they aren't considered 'living', but they tin survive on surfaces for a varying level of time.
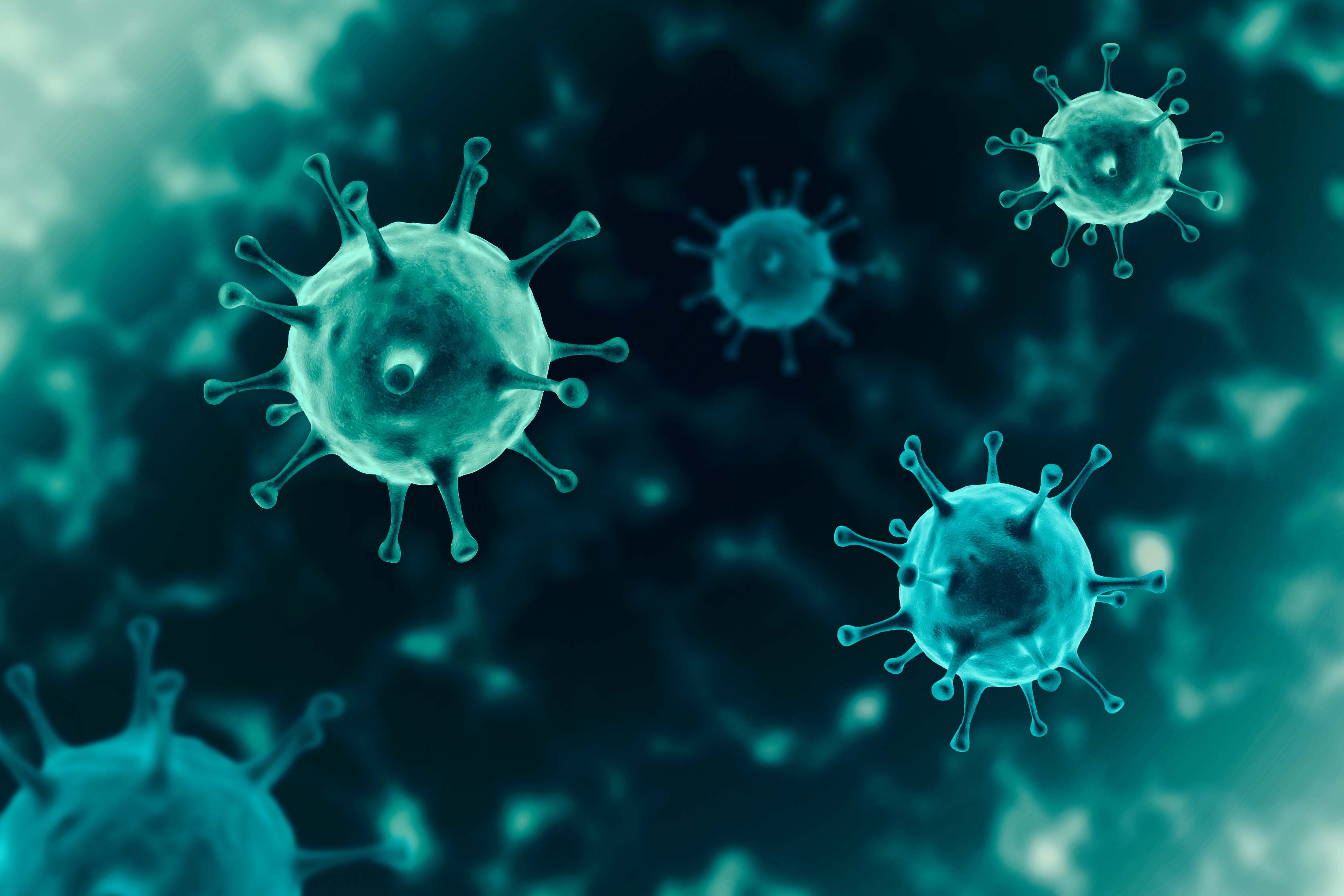
Viruses need to enter a living cell (such every bit a human cell) to be able to reproduce, and once inside they take over all of the cellular machinery and forcefulness the cell to make new virus.
Viruses cause diseases including the flu, canker simplex virus, Ebola, Zika and the formidable common cold.
Viruses can exist quite selective nigh where they live and reproduce–many viruses don't even infect humans. Some viruses but infect bacteria, some but infect plants, and many only infect animals.
However, a virus tin evolve to spring into humans. This oft happens with influenza: for example bird flu or swine influenza which originated in birds and pigs and managed to infect humans. SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-nineteen, probably jumped into humans from bats.
The life cycle of a virus can exist divided into the following stages: entry of the virus into the host prison cell; replication of the viral genome; production of new viral proteins; assembly of those viral proteins into new viruses and so release from the host cell (either by killing the cell or by budding off the host cell membrane) ready to infect new cells.
Why is information technology so of import to tell the difference?
Molecular tools are improving doctors' power to identify viral or bacterial infections more quickly and efficiently—the hope is that doctors can test patients at the GP's surgery or in an emergency and discover out straight away if their illness is caused by a virus or bacteria.

It is important to know the difference between a viral and a bacterial infection then doctors can treat the right affliction, and antibiotics aren't used unnecessarily, contributing to the ascension of antibiotic-resistant superbugs.
It is also why you shouldn't expect your md to prescribe antibiotics if y'all're suffering from a viral infection such equally a common cold.
Researchers at IMB are working on means to exist able to capture and identify bacteria from infections within hours—this currently takes days.
Taking reward of these molecular powerhouses
Researchers are re-engineering the lethal blueprint of bacteria and viruses to detect ways to end their infectious cycles.
At the moment, vaccines are under evolution to protect usa against COVID-xix.
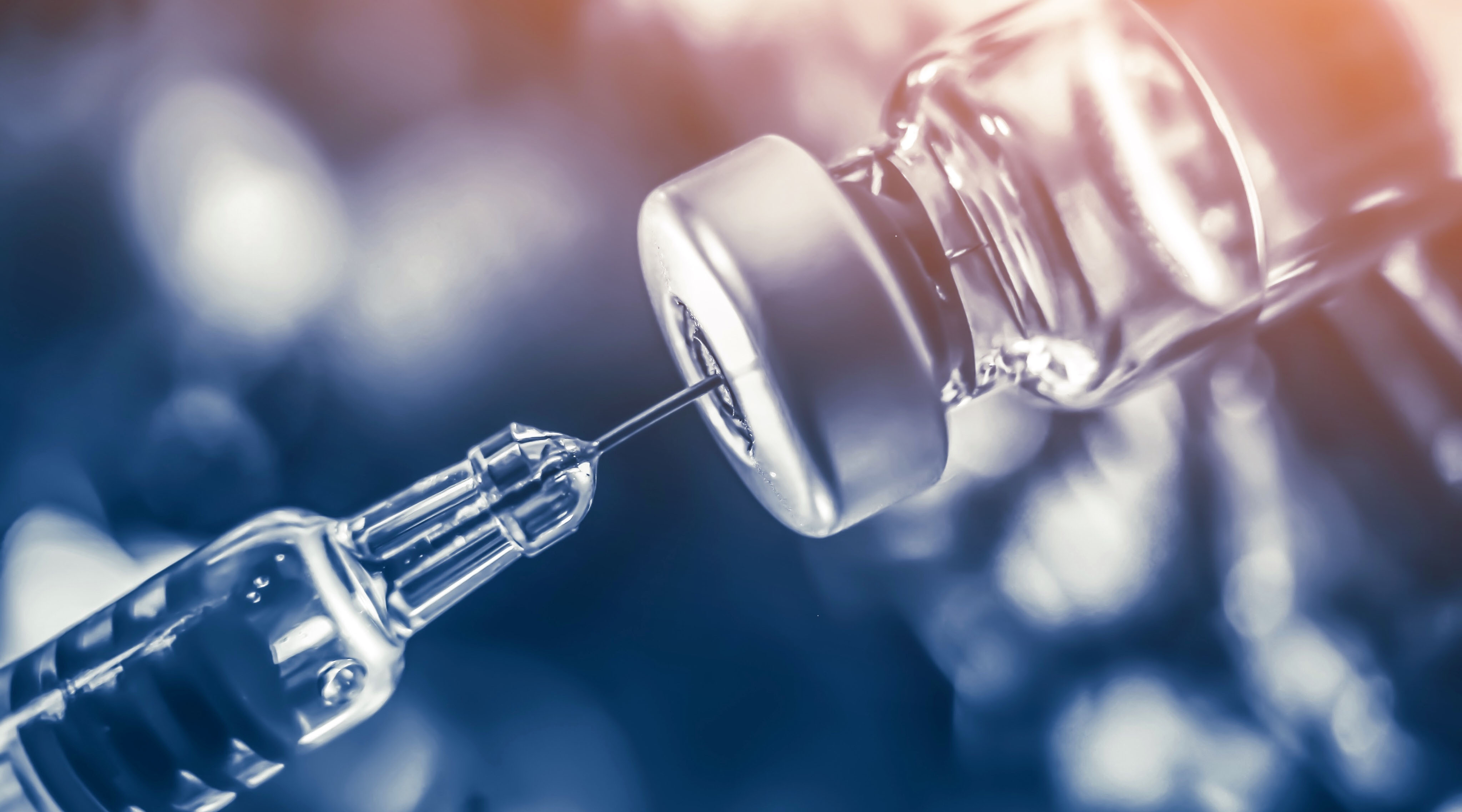 Vaccines prove the allowed system important parts of the virus and so that the immune system tin can set up the tools to fight the existent virus effectively—vaccines fox the allowed system into responding like it has previously seen the virus.
Vaccines prove the allowed system important parts of the virus and so that the immune system tin can set up the tools to fight the existent virus effectively—vaccines fox the allowed system into responding like it has previously seen the virus.
The best studied of these immune 'tools' are antibodies, which stop viruses from getting into new cells. But the immune system as well makes killer cells, which cease viral replication by killing any infected host cells.
Traditionally vaccines are weak or inactivated forms of the virus.
At that place are many potential vaccine candidates in the pipeline globally, made using a broad range of new technologies.
These vaccine technologies include the use of subunit vaccines: researchers brand viral proteins and put them into the body, then that the immune system makes antibodies against those viral proteins.
This method is usually safer and quicker than using live or inactivated virus.
Other technologies trick the trunk to make those viral proteins itself, these include delivery of RNA in liposomes or DNA plasmids in nanoparticles, also as modified safe viruses and existing vaccines.
By studying virus life cycles and how viruses are detected by the immune system, we tin can observe new ways to target the virus and care for viral disease fifty-fifty without a vaccine.
Bacterial and viral infections are often related
While bacterial and viral infections are different, they are often related.
Severe cases of viral pneumonia oft finish upwardly with an associated bacterial infection. This is particularly true with COVID-19, where up to 50% of the severely ill hospitalised patients have developed a bacterial infection. So, despite COVID-19 being caused past a virus, antibiotics are really important to treat the associated bacterial infections.
Equally antibiotic-resistant bacteria are an increasing global problem, researchers at IMB are investigating the surface activeness of bacteria at molecular level and have discovered how they elude the human immune system . They are likewise looking at developing new therapies to treat resistant bacteria, and working to assistance researchers around the world discover new antibiotics.
We're now well on the way to developing preventative therapies, biomarkers and vaccines to foil these elusive microbial assassins from plaguing our world.
Source: https://imb.uq.edu.au/article/2020/04/difference-between-bacteria-and-viruses
0 Response to "Which of the Following Are Systems Bacteria Can Use to Protect Agains Invading Dna"
Post a Comment